Size daha iyi hizmet sunabilmek için çerezleri kullanıyoruz.
Web sitemizde gezinme deneyiminizi geliştirmek, size kişiselleştirilmiş içerik ve hedefli reklamlar göstermek, web sitesi trafiğimizi analiz etmek ve ziyaretçilerimizin nereden geldiğini anlamak için çerezleri ve diğer izleme teknolojilerini kullanıyoruz.
Out Of Stock
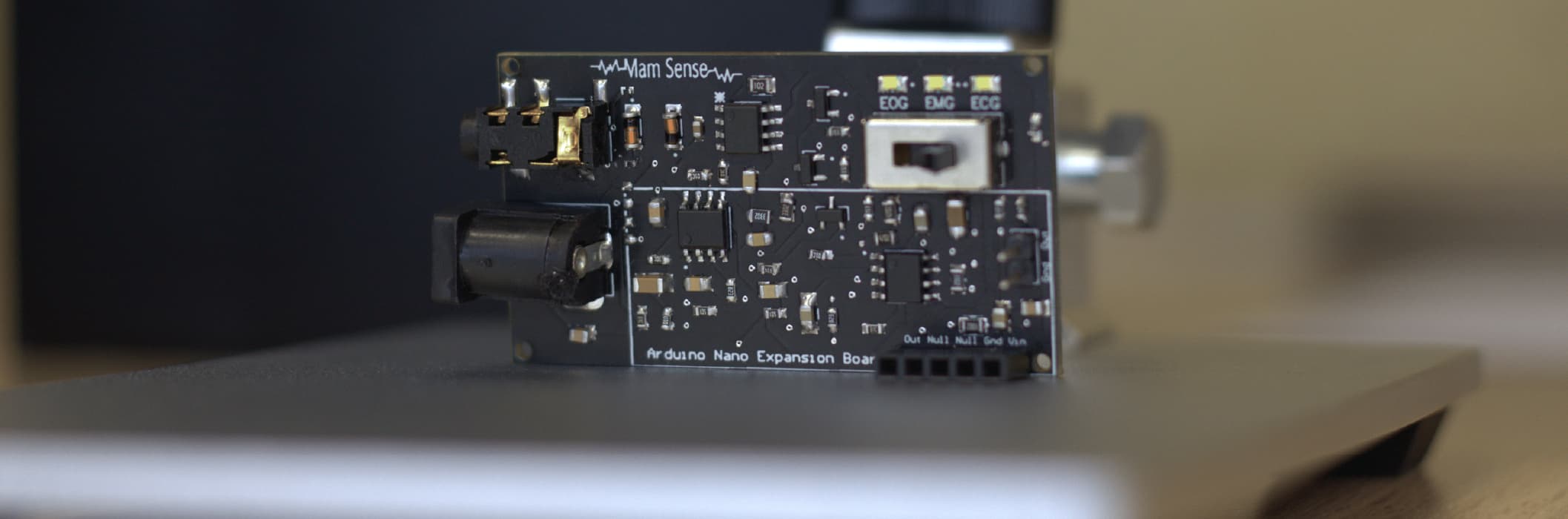
Notify me when its in stockMaM Sense is known by developers for its ability to process 3 different types with a single card: EOG, EKG and EMG. Forwarding as a mode for transmission for a switch path with all three signal paths. Then, according to the analog-to-digital converter to output the board and process the digital signal. The sensor can also be used as an Arduino. As the Nano expansion board is suitable for Arduino Nano sensors, it supplies power to the Arduino's A7 port via a middle DC jack for its outputs as well as to the Arduino Nano. In addition, Arduino codes have been shared by engineers to help developers. You can find Arduino Codes here.
Bioelectric signals are the total electrical current produced by the electrical current on the tissue, organ or cell. Although biopotentials differ according to the tissues and organs from which they originate, they generally have common signal characteristics such as low amplitude (10 μV-10 mV) and low frequency (0 200 Hz). Specialized electrodes and electronic systems are used to obtain these signals for clinical purposes. The system used in this field is usually named with the name of the target organ (such as Electrocardiography, Electroencephalography). Electrodes, amplifiers, signal adaptors, and signal display devices are used in order to measure these potentials, which are of very small amplitude. Surface electrodes that are attached to the skin are commonly used as electrodes (EOG, EMG, ECG) because they do not damage the tissues. Sometimes it is necessary to use a needle electrode to make more local measurements. Because the measured signals are very small, recording problems are encountered at every stage. Problems such as skin conductivity, body movement, electrode noise, interference from the mains, electromagnetic wave interactions further deteriorate the quality of the already small signal.
Although it is possible to measure the biopotentials in every tissue in principle, ECG, EMG and EOG recordings are most frequently performed for diagnostic purposes today. EOG is a method of recording the electrical potential between the cornea and the retina with the help of electrodes placed around the eye. EOG signal amplitude is 0.05-3.5mV and frequency is 1-10 Hz. Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG signal amplitude is 1-10 mV and frequency is 0-500 Hz. Electrocardiography (ECG) is a method for measuring the electrical activity going through the heart by using external (skin)electrodes. ECG signal amplitude is 0.5-1 mV and frequency is 0.1-40 Hz. The aforementioned bioelectric signals are first amplified by using a differential amplifying circuit to have a gain of 101, then filtering is done using a high-pass filter in accordance with the frequency band of the signal. In this filtering stage, the cut-off frequencies of the bioelectric signals were adjusted to be 0.1 Hz, 20 Hz and 0.3 Hz for EOG and EMG and ECG, respectively.